How Long is Electrician School
How long is electrician school? The duration of electrician school varies based on the type of program. Typically, it takes about 1-2 years to complete a diploma or certificate program, while an associate degree program can take up to 2 years. Apprenticeships, essential for practical experience, last 4-5 years.
What is Electrician School
Electrician school is a vocational program that trains individuals to become skilled electricians. These programs cover essential topics such as electrical theory, circuitry, wiring, and safety procedures. Students also gain hands-on experience through lab work and apprenticeships, preparing them for various roles in the electrical industry.

Completing electrician school provides the foundational knowledge and practical skills needed to enter the electrical field. Graduates are equipped to handle residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems. These programs often culminate in certification exams, which validate the student’s expertise and readiness to work professionally as an electrician.
How Long is Electrician School
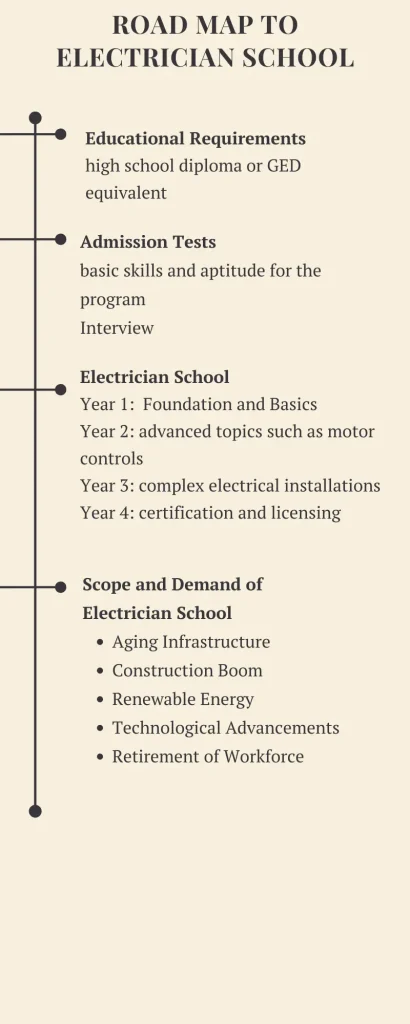
Year 1: In the first year, students are introduced to basic electrical concepts, including electrical theory, mathematics, and safety protocols. Hands-on training begins with simple wiring projects and understanding electrical codes. Students also start learning about tools and equipment used in the trade.
Year 2: The second year focuses on more advanced topics such as motor controls, transformers, and commercial wiring systems. Students continue to develop their practical skills through lab sessions and fieldwork. This year often includes more extensive projects and preparation for apprenticeship placements.
Year 3: By the third year, students are involved in complex electrical installations and troubleshooting. They study programmable logic controllers (PLCs), renewable energy systems, and advanced electrical systems used in industrial settings. Apprenticeships during this year provide real-world experience and mentorship from experienced electricians.
Year 4: The final year prepares students for certification and licensing exams. Coursework includes detailed studies of the National Electrical Code (NEC) and advanced troubleshooting techniques. Students complete their apprenticeships, refining their skills and gaining the experience necessary to enter the workforce as qualified electricians.
How to Enter Medical School
Educational Requirements for Electrician School
High School Diploma or GED: Most electrician schools require applicants to have a high school diploma or GED equivalent.
Prerequisite Courses: Basic knowledge in mathematics, physics, and technical subjects can be beneficial. Some programs may require completion of specific courses in these areas.
Age Requirement: Typically, applicants must be at least 18 years old.
Entry Tests
Aptitude Test: Many electrician programs require applicants to pass an aptitude test that assesses basic math, reading comprehension, and mechanical reasoning skills.
Interview: Some schools may conduct interviews to evaluate an applicant’s interest and suitability for the program.
Application Process
- Research Programs: Investigate different electrician schools and their specific requirements.
- Submit Application: Complete and submit the application form online or in person.
- Provide Transcripts: Submit high school or GED transcripts along with any relevant post-secondary education records.
- Letters of Recommendation: Some programs may require letters of recommendation from teachers, employers, or mentors.
- Personal Statement: Write a personal statement or essay detailing your interest in becoming an electrician.
- Application Fee: Pay the application fee, if applicable.
Financial Aid
Scholarships: Many organizations offer scholarships specifically for students pursuing vocational training in electrical work.
Grants: Federal and state grants may be available based on financial need.
Loans: Students can apply for federal student loans, which often have lower interest rates and flexible repayment options.
Work-Study Programs: Some schools offer work-study programs where students can work part-time to help cover their education costs.
Apprenticeships: Apprenticeships often provide paid on-the-job training, which can help offset educational expenses.
Scope and Demand for Electrician School Graduates
The scope for electrician school graduates is broad and diverse, encompassing various industries and specializations. Electricians are essential in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, where they install, maintain, and repair electrical systems. With the growing emphasis on renewable energy and smart technologies, electricians specializing in solar power, wind energy, and advanced home automation systems are in high demand. Additionally, the construction industry’s steady growth and the increasing need for electrical upgrades in older buildings further enhance job opportunities for skilled electricians.
Demand: The demand for electricians is robust and expected to grow due to several factors:
- Aging Infrastructure: Older buildings require electrical upgrades and maintenance.
- Construction Boom: New construction projects continually need electrical installations.
- Renewable Energy: The shift towards renewable energy sources creates opportunities for electricians specializing in solar and wind power.
- Technological Advancements: The rise of smart homes and businesses requires skilled electricians to install and maintain advanced electrical systems.
- Retirement of Workforce: Many current electricians are nearing retirement, increasing the demand for new professionals in the field.
Electrician school graduates can expect a stable and rewarding career with numerous opportunities for advancement and specialization.
Top 10 Electrician Schools

1.Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech)
Offers a robust electrical engineering program with opportunities for specialization in power systems and automation.
2.Purdue University
Known for its strong electrical and computer engineering programs, offering hands-on training and research opportunities.
3.University of Texas at Austin
Provides an extensive electrical engineering program with a focus on power systems and renewable energy.
4.Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
Renowned for its cutting-edge research and comprehensive electrical engineering curriculum.
5.University of California, Berkeley
Offers a highly-regarded electrical engineering program with various specializations and research opportunities.
6.California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
Known for its rigorous electrical engineering program and strong emphasis on research and innovation.
7.University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Offers a top-ranked electrical engineering program with extensive lab facilities and industry partnerships.
8.Carnegie Mellon University
Provides a comprehensive electrical and computer engineering program with strong industry connections.
9.Stanford University
Known for its excellence in engineering education and research, offering a robust electrical engineering program.
10.Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University (Virginia Tech)
Offers a strong electrical engineering program with a focus on hands-on learning and practical experience.
Factors Affecting the Length of Electrician School
Type of Program:
Certificate Programs: Usually take 6 months to 1 year to complete, focusing on basic skills and entry-level knowledge.
Associate Degree Programs: Typically take 2 years and provide more comprehensive training, including general education courses.
Bachelor’s Degree Programs: Take about 4 years, offering in-depth knowledge and specialization options.
Mode of Study:
Full-Time: Students complete their training faster, usually within the standard duration of the program.
Part-Time: Allows students to work while studying, extending the duration of the program.
Apprenticeships:
Integrated Apprenticeships: Some programs include apprenticeship components, which may extend the overall duration but provide valuable hands-on experience.
Separate Apprenticeships: Completing an apprenticeship after graduation can add several years to the overall training period.
Specializations:
Advanced Specializations: Pursuing additional certifications or specializations in areas like industrial or renewable energy systems can lengthen the training period.
Continuing Education: Ongoing education and professional development can extend learning beyond initial training.
Institutional Requirements:
Curriculum Differences: The specific curriculum and credit requirements of the school can affect the length of the program.
Practical Training Hours: Some programs require a certain number of hands-on training hours, which can impact the overall duration.
State Licensing Requirements:
Varied Regulations: Different states have varying requirements for licensing, which can affect how long it takes to become a licensed electrician.
Additional Exams: Some states may require additional exams or practical assessments, extending the training period.
Prior Experience:
Previous Training: Students with prior electrical training or relevant work experience may be able to complete their programs faster.
Credit Transfer: Transferring credits from other educational institutions can reduce the program length.
Personal Pace:
Learning Speed: Individual learning speeds and study habits can influence how quickly a student progresses through the program.
Personal Commitments: Balancing education with personal or work commitments can affect the time taken to complete the program.
Financial Constraints:
Funding Availability: Financial limitations can affect the ability to enroll full-time or complete the program without interruption.
Work Obligations: Needing to work while studying can extend the program duration.
Technological Advancements:
Emerging Technologies: Keeping up with new technologies and industry standards may require additional training and coursework.
Updated Curricula: Schools frequently update their curricula to include the latest advancements, which can add to the training time.
Final Verdict
Electrician school programs offer a range of training options from short-term certificates to comprehensive degrees. Understanding the various factors that influence program length and the educational requirements is crucial for aspiring electricians. The right training can open doors to a rewarding and skilled career in the electrical industry.
FAQs
1. How long does it typically take to complete electrician school?
The duration varies from 6 months for certificate programs to 4 years for bachelor’s degrees, depending on the program and study mode.
2. What are the basic educational requirements for enrolling in electrician school?
A high school diploma or GED is usually required, along with some prerequisite knowledge in mathematics and technical subjects.
3. Are there financial aid options available for electrician school students?
Yes, students can apply for scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs to help cover educational expenses.
4. Do electrician schools require an entry test?
Many programs require an aptitude test assessing math, reading comprehension, and mechanical reasoning skills, and some may also conduct interviews.
5. What career opportunities are available after completing electrician school?
Graduates can pursue various roles, including residential, commercial, and industrial electricians, with opportunities for further specialization and advancement through certifications and apprenticeships.
