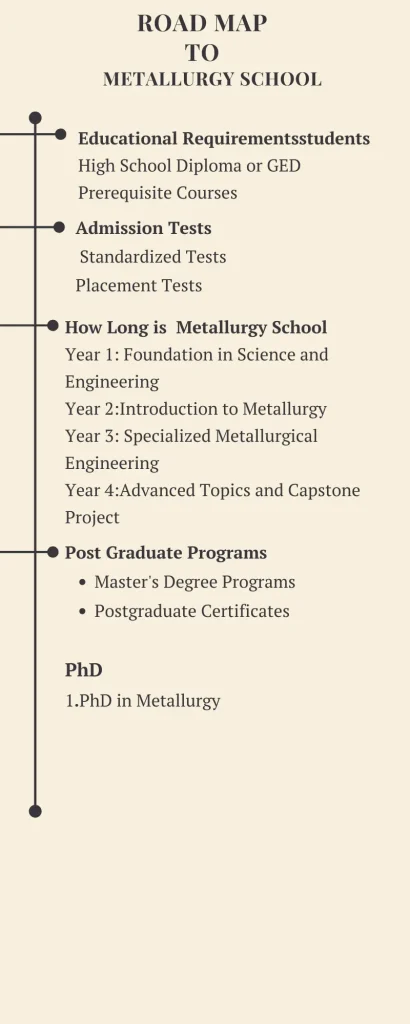
How Long is Metallurgy School? The duration of metallurgy school can vary depending on the program. Typically, a certificate program takes about one year, while an associate degree takes around two years. Bachelor’s degree programs usually last four years. So, how long is metallurgy school depends on the level of education pursued.
What is Metallurgy School
Metallurgy school focuses on the study of metals and their properties, processes, and applications. Students learn about extracting metals from ores, refining techniques, alloy production, and material testing. The curriculum often includes courses in chemistry, physics, and engineering principles related to metals.

In addition to classroom instruction, metallurgy programs often feature hands-on laboratory work and field experiences. These practical components help students gain valuable skills in analyzing and manipulating metals. Graduates of metallurgy school are prepared for careers in various industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, and construction, where they can apply their knowledge to develop and improve metal products.
How Long is Metallurgy School
Year 1: Foundation in Science and Engineering
Courses: General Chemistry, Physics, Calculus, Introduction to Engineering
Focus: Establishing a strong foundation in basic sciences and engineering principles. Students gain an understanding of the fundamental concepts necessary for more specialized metallurgy courses.
Skills: Basic laboratory techniques, analytical thinking, problem-solving
Year 2: Introduction to Metallurgy
Courses: Introduction to Metallurgy, Materials Science, Thermodynamics, Differential Equations
Focus: Introduction to the field of metallurgy and materials science, exploring the physical and chemical properties of metals and their applications.
Skills: Understanding metallurgical processes, basic material characterization, computational skills
Year 3: Specialized Metallurgical Engineering
Courses: Physical Metallurgy, Extractive Metallurgy, Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Metallurgical Thermodynamics
Focus: Delving into more specialized topics such as the mechanical properties of metals, metal extraction processes, and the thermodynamic principles governing metallurgical reactions.
Skills: Advanced laboratory techniques, data analysis, critical thinking
Year 4: Advanced Topics and Capstone Project
Courses: Advanced Materials Characterization, Alloy Design, Corrosion Engineering, Capstone Design Project
Focus: Studying advanced topics in metallurgy and materials science, with an emphasis on real-world applications and problem-solving. The capstone project integrates knowledge gained throughout the program.
Skills: Project management, teamwork, advanced analytical and research skills
How to Enter Metallurgy School
Educational Requirements for Metallurgy School
High School Diploma or Equivalent
Completion of high school with a strong foundation in science and mathematics.
Prerequisite Courses
Mathematics (Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Calculus)
Sciences (Chemistry, Physics, Biology)
English and Communication Skills
Entry Tests
Standardized Tests
SAT or ACT scores (varies by institution)
TOEFL or IELTS for international students (if applicable)
Subject Tests
Advanced Placement (AP) tests in relevant subjects like Chemistry, Physics, or Calculus (optional but advantageous)
Application Process
Application Form
Completed application form (online or paper-based) available on the institution’s website.
Transcripts
Official high school transcripts and any college coursework if applicable.
Letters of Recommendation
Typically two to three letters from teachers, counselors, or professionals familiar with the student’s academic abilities and character.
Personal Statement/Essay
A well-crafted essay detailing the student’s interest in metallurgy, career goals, and why they want to attend that particular school.
Resume/CV
A resume highlighting extracurricular activities, volunteer work, relevant work experience, and any honors or awards.
Application Fee
Payment of a non-refundable application fee (amount varies by institution).
Financial Aids
Scholarships
Merit-based scholarships for academic excellence.
Need-based scholarships for students demonstrating financial need.
Scholarships specifically for students pursuing degrees in engineering or metallurgy.
Grants
Federal Pell Grants and other state or institutional grants.
Loans
Federal student loans (subsidized and unsubsidized).
Private student loans from banks or financial institutions.
Work-Study Programs
Part-time employment opportunities provided by the school to help students earn money while studying.
Fellowships and Assistantships
Research or teaching assistant positions that provide a stipend and/or tuition waiver (usually for upper-level undergraduates or graduate students).
Financial Aid Office
Access to financial aid counselors who can help students understand and apply for various financial aid options.
These components ensure that prospective students are well-prepared to apply for and succeed in a metallurgy program, with the financial support necessary to complete their education.
Post Graduate and PhD Programs
Postgraduate Programs in Metallurgy
Master’s Degree in Metallurgy
Duration:
typically 1.5 to 2 years
Educational Requirements:
Bachelor’s Degree: In metallurgy, materials science, or a related engineering field.
GPA Requirements: Minimum GPA as specified by the institution (usually around 3.0 or higher).
Application Process:
Application Form: Completed online application.
Transcripts: Official transcripts from all previous post-secondary institutions.
Letters of Recommendation: Typically two to three letters from academic or professional references.
Personal Statement/Essay: Detailing research interests, career goals, and reasons for pursuing a master’s degree in metallurgy.
Resume/CV: Highlighting academic achievements, research experience, publications, and relevant work experience.
Standardized Tests: GRE scores (if required by the institution).
Application Fee: Non-refundable fee (amount varies by institution).
Curriculum:
Core Courses: Advanced thermodynamics, physical metallurgy, materials characterization, phase transformations.
Electives: Courses in specialized topics such as nanomaterials, corrosion, biomaterials, and computational materials science.
Research Component: Independent research project or thesis under the guidance of a faculty advisor.
Internships/Co-op Programs: Opportunities for industry experience and practical application of skills.
Financial Aid:
Graduate Assistantships: Teaching or research assistant positions providing stipends and tuition waivers.
Fellowships: Competitive fellowships offered by the institution or external organizations.
Grants and Scholarships: Merit-based or need-based financial support.
PhD Programs in Metallurgy
Duration: Typically 3 to 5 years
Educational Requirements:
Master’s Degree: In metallurgy, materials science, or a related engineering field (some programs may admit students directly from a bachelor’s degree).
GPA Requirements: Minimum GPA as specified by the institution (usually around 3.5 or higher).
Application Process:
Application Form: Completed online application.
Transcripts: Official transcripts from all previous post-secondary institutions.
Letters of Recommendation: Typically three letters from academic or professional references.
Research Proposal: Outline of intended research topic and objectives.
Personal Statement/Essay: Detailing research interests, career goals, and reasons for pursuing a PhD in metallurgy.
Resume/CV: Highlighting academic achievements, research experience, publications, and relevant work experience.
Standardized Tests: GRE scores (if required by the institution).
Application Fee: Non-refundable fee (amount varies by institution).
Curriculum:
Core Courses: Advanced topics in materials science, metallurgy, and related fields.
Electives: Specialized courses tailored to the student’s research interests.
Comprehensive Exams: Written and/or oral exams to assess knowledge and readiness for research.
Research Component: Original research leading to a dissertation, under the guidance of a faculty advisor.
Dissertation Defense: Public presentation and defense of the dissertation research.
Financial Aid:
Research Assistantships: Positions funded by research grants, providing stipends and tuition waivers.
Teaching Assistantships: Positions involving teaching responsibilities, providing stipends and tuition waivers.
Fellowships: Competitive fellowships offered by the institution or external organizations.
Grants and Scholarships: Merit-based or need-based financial support.
These postgraduate and PhD programs prepare students for advanced careers in metallurgy, academia, research, and industry, equipping them with in-depth knowledge and specialized skills in the field.
Top 10 Metallurgy Schools

1.Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
Location: Cambridge, MA, USA
Notable Programs: Materials Science and Engineering, Metallurgy
Highlights: Renowned for cutting-edge research, state-of-the-art facilities, and a strong emphasis on innovation.
2.Stanford University
Location: Stanford, CA, USA
Notable Programs: Materials Science and Engineering
Highlights: Offers a robust curriculum, interdisciplinary research opportunities, and strong industry connections.
3.University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley)
Location: Berkeley, CA, USA
Notable Programs: Materials Science and Engineering, Metallurgical Engineering
Highlights: Known for its research excellence, diverse faculty, and comprehensive academic programs.
4.California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
Location: Pasadena, CA, USA
Notable Programs: Materials Science and Engineering
Highlights: Focuses on high-impact research, small class sizes, and personalized mentorship.
5.University of Cambridge
Location: Cambridge, England, UK
Notable Programs: Materials Science and Metallurgy
Highlights: Offers world-class research facilities, a historic reputation for academic excellence, and strong industry partnerships.
6.Imperial College London
Location: London, England, UK
Notable Programs: Materials Science and Engineering, Metallurgy
Highlights: Emphasizes innovation, research-driven curriculum, and extensive industry collaborations.
7.University of Oxford
Location: Oxford, England, UK
Notable Programs: Materials Science
Highlights: Provides a rich academic tradition, cutting-edge research, and a collaborative learning environment.
8.University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Location: Urbana and Champaign, IL, USA
Notable Programs: Materials Science and Engineering
Highlights: Known for its comprehensive research facilities, strong faculty, and diverse academic offerings.
9.ETH Zurich – Swiss Federal Institute of Technology
Location: Zurich, Switzerland
Notable Programs: Materials Science, Metallurgy
Highlights: Offers a strong emphasis on interdisciplinary research, global collaboration, and high academic standards.
10.University of Tokyo
Location: Tokyo, Japan
Notable Programs: Materials Engineering, Metallurgy
Highlights: Renowned for its research excellence, innovative technology development, and strong industry ties.
These institutions are recognized for their exceptional programs in metallurgy and materials science, providing students with unparalleled educational and research opportunities in the field.
Factors Affecting the Length of Metallurgy School
Program Type
Certificate Programs: Generally last about 1 year, focusing on foundational skills and specific technical knowledge.
Associate Degrees: Typically 2 years, combining general education with specialized metallurgy courses.
Bachelor’s Degrees: Usually 4 years, offering a comprehensive education including theoretical and practical aspects of metallurgy.
Master’s Degrees: Typically 1.5 to 2 years, focused on advanced topics and research.
PhD Programs: Generally 3 to 5 years, centered around original research and dissertation work.
Institutional Requirements
Curriculum Design: The specific structure and content of the program can impact duration.
Credit Requirements: The total number of credits required to graduate varies by institution.
Course Availability: Frequency and scheduling of required courses can affect the time needed to complete the program.
Student’s Background
Prior Education: Students with relevant coursework or degrees may be able to transfer credits, shortening their study duration.
Full-time vs. Part-time Enrollment: Full-time students typically complete programs faster than part-time students.
Preparatory Courses: Students lacking prerequisite knowledge may need additional time to complete preparatory courses.
Research and Internship Opportunities
Research Projects: Engaging in extensive research projects, especially at the graduate level, can extend the duration of study.
Internships/Co-op Programs: Participation in internships or cooperative education programs may extend the time required to graduate but provide valuable practical experience.
Understanding these factors can help prospective students plan their educational paths in metallurgy more effectively, considering their personal circumstances and goals.
Final Verdict
Understanding the factors affecting the length of metallurgy school helps prospective students plan their educational paths effectively. Program type, institutional requirements, student background, research opportunities, and personal commitments all influence the duration of study, ensuring that students can make informed decisions about their academic and career goals.
FAQs
1.What prerequisites are needed for a metallurgy degree?
Prerequisites typically include high school courses in chemistry, physics, mathematics, and sometimes introductory engineering subjects.
2.How long does it take to complete a bachelor’s degree in metallurgy?
A bachelor’s degree in metallurgy usually takes about four years of full-time study to complete.
3.What are the career prospects after graduating from metallurgy school?
Graduates can pursue careers in industries such as aerospace, automotive, manufacturing, and materials research, working as metallurgists, materials engineers, and researchers.
4.What financial aid options are available for metallurgy students?
Financial aid options include scholarships, grants, fellowships, work-study programs, and student loans, with specific opportunities varying by institution.
5.Can I pursue a metallurgy degree part-time while working?
Yes, many institutions offer part-time study options to accommodate working students, though this will extend the duration of the program.
