How Long is Realtor School
How long is realtor school? Realtor school typically takes 2 to 6 months to complete, depending on the state’s requirements and the chosen course format. Students must complete pre-licensing education, pass a state exam, and fulfill additional training to become licensed real estate agents.
What is Realtor School
Realtor school is an educational program designed to prepare individuals for a career in real estate. These programs cover essential topics such as property laws, real estate practices, ethics, and market analysis. By completing the required coursework, aspiring realtors gain the knowledge and skills needed to pass the state licensing exam and succeed in the competitive real estate market.

In realtor school, students learn through a combination of lectures, practical exercises, and examinations. The curriculum often includes both in-person and online courses, allowing flexibility for students with varying schedules. Successful completion of the program not only equips future realtors with industry-specific knowledge but also provides a solid foundation for building a successful career in real estate.
How Long is REALTOR School
Realtor school does not follow the traditional undergraduate program structure, but for clarity, we can break down the typical timeline and stages involved in becoming a realtor:
Year 1: Pre-Licensing Education
- Months 1-6: Enroll in a pre-licensing course, which can be completed in a classroom setting or online. The duration varies by state but typically ranges from 60 to 180 hours of instruction.
- Months 7-12: Prepare for and take the state real estate licensing exam. This involves studying the material covered in the pre-licensing course and possibly attending additional review sessions.
Year 2: Gaining Practical Experience
- Months 1-6: After passing the licensing exam, join a real estate brokerage as a new agent. This period involves practical training, mentorship, and gaining hands-on experience in the field.
- Months 7-12: Continue working under the supervision of experienced realtors, building a client base, and learning the intricacies of real estate transactions.
Year 3: Advanced Training and Specialization
- Months 1-6: Pursue additional certifications or designations to specialize in areas such as commercial real estate, property management, or residential sales. These certifications require further coursework and exams.
- Months 7-12: Continue developing expertise in the chosen specialization, attending workshops, seminars, and continuing education courses to stay updated on industry trends and regulations.
HOW TO ENTER REALTOR SCHOOL
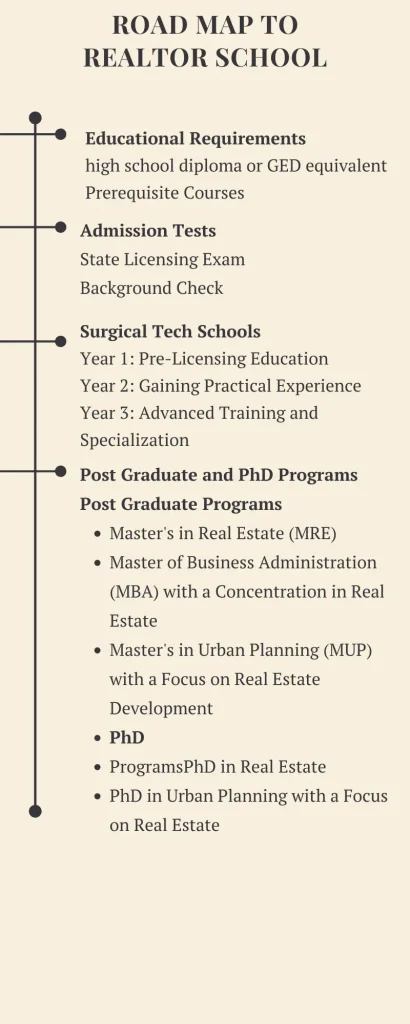
Educational Requirements
High School Diploma or Equivalent:
Most states require a high school diploma or GED as a minimum educational qualification.
Pre-Licensing Education:
Completion of state-approved pre-licensing courses, ranging from 60 to 180 hours, depending on the state’s requirements.
Additional Courses:
Some states may require additional coursework in specific areas such as ethics, contracts, or real estate law.
Entry Tests
State Licensing Exam:
Must pass a state-specific real estate licensing exam, which typically includes both national and state-specific sections.
The exam tests knowledge of real estate principles, practices, and laws.
Background Check:
Many states require a background check and fingerprinting as part of the licensing process.
Application Process
Choose a Pre-Licensing Course:
Select an accredited real estate school offering state-approved pre-licensing courses.
Complete Pre-Licensing Education:
Attend and complete the required hours of coursework.
Submit Application:
Submit an application to the state real estate commission, including proof of completed education, background check results, and application fees.
Schedule and Pass the Licensing Exam:
Schedule the state licensing exam through the authorized testing provider.
Pass the exam and receive your real estate license.
Join a Brokerage:
Join a licensed real estate brokerage to begin practicing as a realtor.
Financial Aid
Scholarships:
Some real estate schools and professional organizations offer scholarships to aspiring realtors based on merit or financial need.
Grants:
Grants may be available through various state programs or industry associations to cover the cost of pre-licensing education.
Employer Sponsorship:
Some real estate brokerages offer sponsorship programs, covering the cost of education and licensing in exchange for a commitment to work with the brokerage for a specified period.
Payment Plans:
Many real estate schools offer flexible payment plans, allowing students to pay for courses in installments.
Financial Aid Programs:
Investigate state-specific financial aid programs designed to support individuals pursuing careers in real estate.
Post Graduate and PhD Programs
Realtor school itself does not typically offer postgraduate or PhD programs as it is primarily focused on pre-licensing education and continuing education for real estate professionals. However, individuals seeking advanced education in real estate can pursue higher academic degrees related to the field. Here are the options:
Postgraduate Programs
- Master’s in Real Estate (MRE):
Curriculum: Focuses on advanced real estate principles, real estate finance, market analysis, property management, urban development, and investment strategies.
Duration: Typically 1-2 years.
Admission Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, GMAT/GRE scores, relevant work experience, and letters of recommendation.
- Master of Business Administration (MBA) with a Concentration in Real Estate:
Curriculum: Combines core business courses with specialized real estate courses, covering topics such as real estate finance, investment, development, and strategic management.
Duration: Typically 2 years.
Admission Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, GMAT/GRE scores, relevant work experience, and letters of recommendation.
- Master’s in Urban Planning (MUP) with a Focus on Real Estate Development:
Curriculum: Emphasizes urban planning, sustainable development, real estate development, and public policy.
Duration: Typically 2 years.
Admission Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, relevant coursework, and letters of recommendation.
PhD Programs
- PhD in Real Estate:
Curriculum: In-depth research on real estate economics, market dynamics, real estate finance, property law, and urban development.
Duration: Typically 3-5 years.
Admission Requirements: Master’s degree in a related field, GRE scores, research proposal, and letters of recommendation.
Outcome: Prepares graduates for careers in academia, research, and high-level consultancy.
- PhD in Urban Planning with a Focus on Real Estate:
Curriculum: Advanced study of urban planning, land use, real estate development, and policy analysis.
Duration: Typically 3-5 years.
Admission Requirements: Master’s degree in urban planning or a related field, GRE scores, research proposal, and letters of recommendation.
Outcome: Equips graduates for careers in academia, urban planning, and policy-making.
Top 10 REALTOR Schools
Choosing a top real estate school can depend on various factors including accreditation, reputation, faculty expertise, and program offerings. Here are ten reputed real estate schools in the United States:

- University of Pennsylvania – Wharton School
Offers a comprehensive real estate program with a focus on finance, development, and urban economics.
- New York University – Schack Institute of Real Estate
Renowned for its real estate programs, offering degrees at the undergraduate, graduate, and executive levels.
- University of California, Berkeley – Haas School of Business
Offers a top-ranked real estate program emphasizing finance, development, and policy.
- University of Wisconsin-Madison – Wisconsin School of Business
Known for its strong real estate curriculum with a focus on investment and urban land economics.
- University of Southern California – Marshall School of Business
Offers a comprehensive real estate program with strengths in development, finance, and global real estate markets.
- Columbia University – Columbia Business School
Offers a rigorous real estate curriculum with concentrations in finance, development, and investment.
- University of Texas at Austin – McCombs School of Business
Known for its real estate program with a focus on finance, investment, and sustainable development.
- Cornell University – Baker Program in Real Estate
Offers a specialized graduate program focusing on real estate finance, investment, and development.
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) – Center for Real Estate
Offers a renowned real estate program with a focus on technology, sustainability, and urban development.
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill – Kenan-Flagler Business School
Offers a comprehensive real estate program with strengths in finance, development, and investment strategies.
Factors Affecting the Length of REALTOR School
The length of realtor school, or the time it takes to complete the educational requirements for becoming a licensed real estate agent, can vary based on several factors:
State Requirements: Each state sets its own requirements for pre-licensing education. The number of required course hours can range from 60 to 180 hours, depending on the state’s regulations.
Course Format: The format of the pre-licensing courses can impact the length of time required. Courses may be offered in traditional classroom settings, online, or as hybrid options, allowing flexibility in scheduling.
Study Pace: The pace at which a student completes the coursework can affect the overall duration. Some individuals may choose accelerated programs to finish quickly, while others may opt for part-time study to accommodate work or other commitments.
Additional Requirements: In addition to completing pre-licensing education, some states require applicants to fulfill additional requirements such as passing background checks, completing ethics courses, or meeting specific age criteria.
Exam Preparation: The time taken to prepare for and pass the state licensing exam varies among individuals. Some may need more time for studying and review, while others may feel confident with less preparation.
Practical Experience: While not part of formal realtor school, gaining practical experience through internships or mentorship programs can be beneficial. This experience may be integrated into the overall timeline depending on the individual’s approach to learning and career readiness.
Final Verdict
In conclusion, the length of realtor school varies depending on several factors, including state requirements, course format, study pace, and additional licensing criteria. Understanding these factors is crucial for aspiring real estate agents aiming to navigate the educational path efficiently. By carefully planning and considering these variables, individuals can determine “how long is realtor school” for their specific circumstances and successfully prepare for licensure in the dynamic field of real estate.
FAQs
How long is realtor school?
Realtor school typically ranges from several weeks to a few months, depending on state requirements and the pace at which courses are completed.
What are the educational requirements for becoming a realtor?
Requirements vary by state but generally include completing pre-licensing education, passing a state exam, and meeting additional criteria such as background checks and ethics training.
How much does realtor school cost?
Costs vary based on the real estate school, location, and course format (online vs. in-person). Generally, expect to budget for tuition fees, study materials, and exam fees.
What is the difference between a real estate agent and a realtor?
A real estate agent is licensed to help clients buy, sell, or rent properties, whereas a realtor is a member of the National Association of Realtors (NAR) and adheres to a code of ethics and professional standards.
Can I take realtor school courses online?
Yes, many real estate schools offer online courses that fulfill pre-licensing education requirements. Online learning provides flexibility for students to study at their own pace and convenience.
