How Long is Ultrasound Tech School
How Long is Ultrasound Tech School? The duration of ultrasound tech school varies, typically taking 1 to 2 years to complete. How long is ultrasound tech school depends on the type of program chosen, with certificate programs being shorter and associate degree programs taking longer to finish.
What is Ultrasound Tech School
Ultrasound tech school trains students to become skilled sonographers, professionals who use ultrasound technology to capture images of the body’s internal structures. The curriculum covers anatomy, patient care, medical ethics, and hands-on training with ultrasound equipment. Graduates are prepared to work in hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic imaging centers.
In ultrasound tech school, students learn to operate sophisticated imaging machinery, interpret sonographic images, and assist physicians in diagnosing medical conditions. The program combines classroom instruction with clinical experience, ensuring students gain the knowledge and practical skills needed for a successful career in medical imaging. This comprehensive education prepares graduates for certification and employment in the healthcare industry.
How Long is Ultrasound Tech School Program
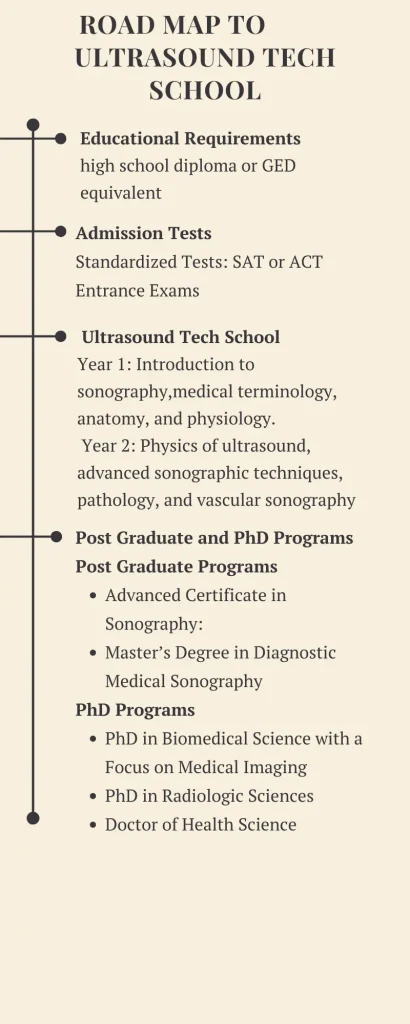
Year 1: Basic Courses
Core Courses: Introduction to sonography, medical terminology, anatomy, and physiology.
Basic Skills: Patient care basics, medical ethics, and introductory ultrasound techniques.
Clinical Experience: Initial hands-on training in a supervised clinical setting.
Year 2: Advanced Courses:
Advanced Courses: Physics of ultrasound, advanced sonographic techniques, pathology, and vascular sonography.
Specialization: Opportunities to focus on specific areas such as obstetrics, gynecology, abdominal, or cardiac sonography.
Extended Clinical Rotations: Increased time in clinical settings to refine practical skills and gain real-world experience.
How to Enter Ultrasound Tech School
Educational Requirements
High School Diploma or Equivalent: Completion of high school education or GED.
Prerequisite Courses: Biology, chemistry, physics, and math courses often required.
Health and Safety Compliance: Vaccinations, background checks, and drug screening.
Entry Tests
Standardized Tests: SAT or ACT scores may be required.
Entrance Exams: Some programs might require specific entrance exams focused on healthcare or sonography.
Language Proficiency: TOEFL or IELTS for non-native English speakers.
Application Process
Application Form: Complete the school’s application form, which is often available online.
Transcripts: Submit high school and any post-secondary education transcripts.
Letters of Recommendation: Provide letters from teachers, employers, or professionals in the healthcare field.
Personal Statement: Write an essay explaining why you want to become an ultrasound technician.
Interview: Some programs may require an interview as part of the selection process.
Financial Aids
Federal and State Grants: Apply for grants such as the Pell Grant through the FAFSA.
Scholarships: Look for scholarships specifically for healthcare or sonography students.
Work-Study Programs: Opportunities to work part-time while studying.
Student Loans: Federal and private student loans to cover tuition and other expenses.
Institutional Aid: Financial aid provided directly by the school, including merit-based and need-based scholarships.
Post Graduate and PhD Programs for Ultrasound Tech School
Post Graduate Programs:
- Advanced Certificate in Sonography: Aimed at certified sonographers seeking to specialize further in areas like vascular, cardiac, or musculoskeletal sonography.
- Master’s Degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography: For those looking to advance into educational, research, or administrative roles within the field.
- Graduate Diploma in Medical Ultrasound: Provides specialized training for advanced practice in sonography, often including hands-on clinical training.
- Fellowship Programs: Focused training in niche areas of sonography, offering opportunities to work closely with experts and gain in-depth knowledge.
PhD Programs:
- PhD in Biomedical Science with a Focus on Medical Imaging: Emphasizes research in ultrasound technology, its applications, and innovations.
- PhD in Radiologic Sciences: Allows for advanced research in medical imaging techniques, including ultrasound, and prepares graduates for careers in academia or high-level research.
- Doctor of Health Science (DHSc): Designed for healthcare professionals looking to pursue leadership, policy, and educational roles, with opportunities to focus on ultrasound technology.
Top 10 Ultrasound Tech Schools

- University of California, San Diego (UCSD)
Offers a highly respected program with extensive clinical training and research opportunities.
- University of Washington
Known for its rigorous curriculum and state-of-the-art facilities in medical imaging.
- Johns Hopkins University
Provides comprehensive training with access to one of the top medical research institutions.
- Mayo Clinic School of Health Sciences
Features exceptional clinical education and hands-on training in a leading healthcare setting.
- University of Missouri-Columbia
Offers a well-rounded program with strong emphasis on both theoretical and practical training.
- Oregon Institute of Technology
Known for its focused curriculum and extensive clinical rotation opportunities.
- Rush University
Provides a strong program with excellent clinical training and research facilities.
- Thomas Jefferson University
Offers a variety of specializations within its ultrasound tech program and strong clinical partnerships.
- University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
Features a comprehensive program with a good balance of classroom instruction and clinical practice.
- University of Iowa
Known for its solid program and strong emphasis on research and clinical training.
Factors Affecting the Length of Ultrasound Tech School
Type of Program:
Certificate Programs: Typically last about 1 year and focus on basic sonography skills.
Associate Degree Programs: Usually take 2 years to complete and provide a more comprehensive education, including general education courses.
Bachelor’s Degree Programs: Can take 4 years, offering an in-depth education with a broader scope, including advanced sonographic techniques and research opportunities.
Part-Time vs. Full-Time Enrollment:
Full-Time Programs: Allow students to complete their studies more quickly, generally following a structured timeline.
Part-Time Programs: Provide flexibility for students who may be working or have other commitments, but they extend the overall duration of the program.
Clinical Rotation Requirements:
Programs with extensive clinical training components may take longer to complete, as students need to fulfill a specific number of clinical hours.
The availability and scheduling of clinical placements can also impact the program length.
Specializations:
Choosing to specialize in a particular area of sonography (e.g., vascular, cardiac, or pediatric) may require additional coursework and clinical hours, extending the duration of the program.
Prerequisite Courses:
Some programs require students to complete prerequisite courses in subjects like anatomy, physiology, and physics before starting the core sonography curriculum. Completing these prerequisites can add to the overall time required.
Institutional Variations:
Different schools may have varying program lengths based on their curriculum design, clinical affiliations, and accreditation standards.
Accelerated Programs:
Some institutions offer accelerated programs that allow students to complete their education in a shorter timeframe through an intensive, fast-paced curriculum.
Credit Transfers:
Students who have previously completed relevant coursework or hold a degree in a related field may be able to transfer credits, potentially reducing the time needed to complete the program.
Final Verdict
Understanding the factors influencing the duration of ultrasound tech school is crucial for prospective students. Program type, clinical requirements, and specialization choices significantly impact the length of study, offering various pathways to becoming a skilled sonographer.
FAQs
What are the educational requirements for ultrasound tech school?
Typically, you need a high school diploma or GED equivalent.
Prerequisite courses in subjects like biology, chemistry, physics, and math are often required.
Some programs may also require health and safety compliance, including vaccinations and
background checks.
How long does it typically take to complete ultrasound tech school?
The length varies based on the type of program:
Certificate programs: About 1 year.
Associate degree programs: Approximately 2 years.
Bachelor’s degree programs: Generally take 4 years.
Part-time programs may extend the duration, while accelerated options may shorten
What is the difference between certificate, associate, and bachelor’s degree programs in ultrasound technology?
Certificate programs focus on basic sonography skills and can be completed in about 1 year. Associate degree programs offer more comprehensive education with general courses, taking about 2 years. Bachelor’s degrees provide in-depth study including advanced techniques and research opportunities, typically spanning 4 years.
Are there online options available for studying ultrasound technology?
Yes, many institutions offer online options for studying ultrasound technology, providing flexibility through virtual lectures and clinical placements.
What career opportunities are available after completing ultrasound tech school?
After completing ultrasound tech school, career opportunities include roles as diagnostic medical sonographers, vascular sonographers, echocardiographers, and ultrasound technologists in hospitals, clinics, and imaging centers.
